Soil is our life support system, anchoring roots, storing water, and providing nutrients for life on Earth.
Soil is vital to Otago’s economy and the health of our land. Over time, different soils have formed across the region due to varying geology, climate, topography and the organisms that live in and on the soil. In the simplest terms, soil has three ingredients:
- Minerals – rocks broken and weathered to varying degrees
- Organics – living organisms and decomposed plants and animals
- Space – voids in the soil that are filled with water or air
In each soil type, these ingredients are made up in specific ways and their relative proportions differ. This affects the ways that each soil type behaves and can be managed.

The New Zealand Soil Classification (NZSC) system recognises 15 soil orders that differ in their characteristics, behaviour and appearance. Around 10 of these soil orders are found in Otago, with eight having regional extents greater than 1%.
The dry basins of Central Otago form dense alkaline Semiarid soils, while the high rainfall alpine valleys host acidic Podzols. Between these extremes, the extensive Pallic and Brown soils are found in hills and high country across the region. Young Raw and Recent soils are formed when the parent material erodes and is deposited on slopes and by rivers. Gley soils are predominantly wet and found where drainage is poor. Melanic soils have dark topsoils formed from limestone and volcanic rock.
Maps of NZSC soil orders present in Otago.
Compare between the Fundamental Soil Layer, S-Map and growOTAGO soil map layers.
(This will only take a moment to load)
Spatial mapping of soil is of great importance to landowners. It means they can manage their operations by understanding the risks and opportunities of different soil types. Soil maps are also used to model nutrient and sediment movement. You can find three soil maps for Otago online – they vary in their cover and reliability.
- The Fundamental Soil Layer combines data from the National Soil Data Repository and the New Zealand Land Resource Inventory databases. It is the only soil map that covers the whole country. It is informative at regional and national scales but less so at finer scales (such as for individual properties). This map will be replaced by S-map.
- The growOTAGO map combines pre-1992 soil maps and soil surveys from the early 2000s. It has full coverage of Otago, mapped by lowlands and uplands. It is the next best soil map after S-map, but should only be used in areas that the S-map doesn’t cover.
- S-map is based on past and ongoing soil surveys. It is the best and most comprehensive soil mapping resource available in Aotearoa New Zealand, but it is not complete – around 30% of Otago is mapped (most of the lowlands). The aim is to complete national coverage by 2030.
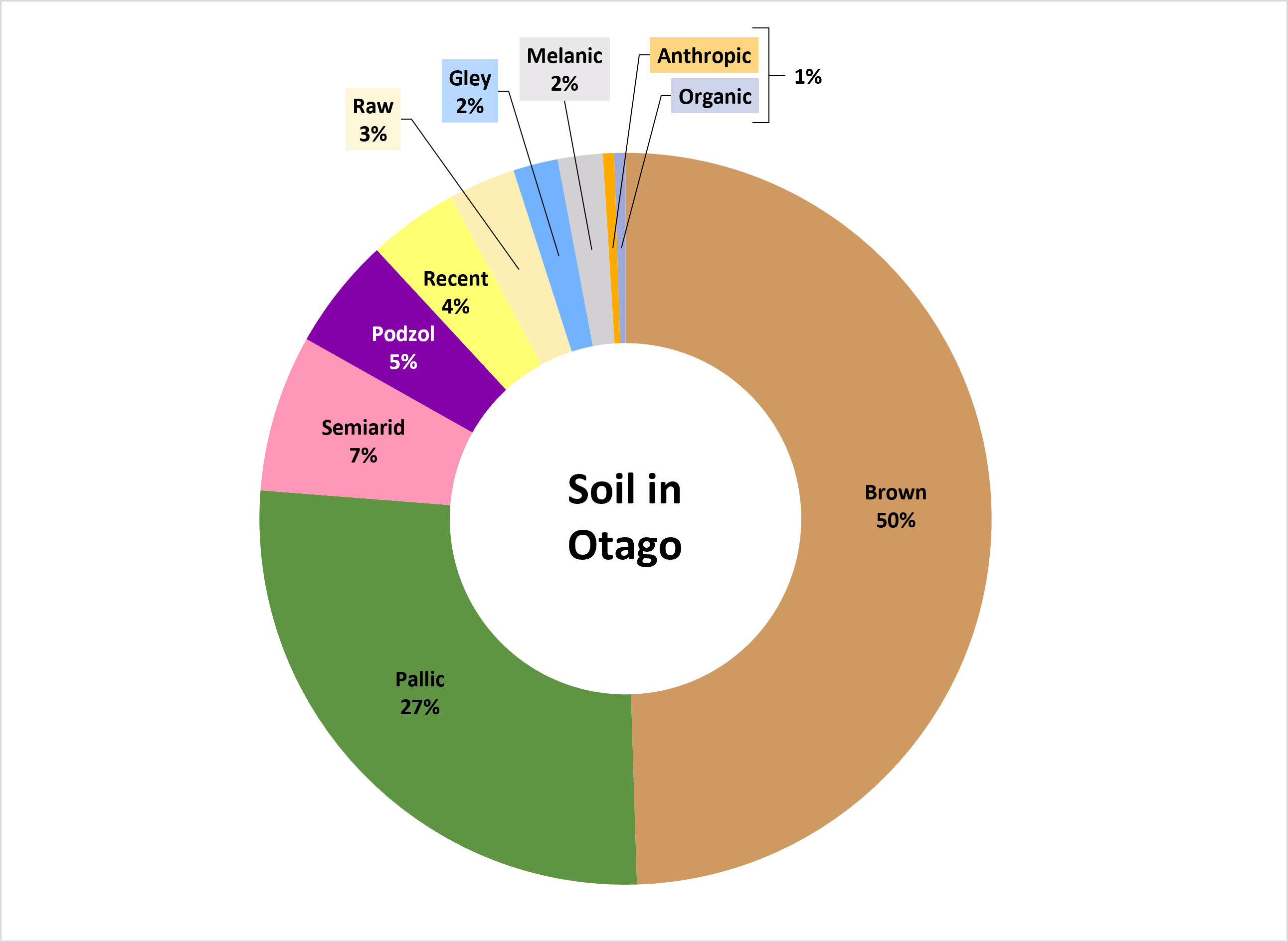
You can download factsheets for the eight most extensive soil orders below. The factsheets show the different soil groups in each order, along with soil mapping resources, photos and notes on how to manage the soils.
Soil order: All
Area: 99%
Key characteristics: General information on all soil orders
Soil order: Brown
Area: 50%
Key characteristics: Low natural fertility but with generally good drainage and rooting depth unless acidic or shallow
Soil order: Pallic
Area: 27%
Key characteristics: Medium to high fertility with imperfect to poor drainage due to high density and/or presence of pans, which limit rooting.
Soil order: Semiarid
Area: 7%
Key characteristics: Well drained soils with moderate fertility limited by rooting depth due to density, stoniness and dryness.
Soil order: Podzol
Area: 5%
Key characteristics: Low fertility, prolonged wetness high subsoil density and/or pans limit plant productivity. High organic matter contents.
Soil order: Recent
Area: 4%
Key characteristics: Highly fertile due to frequent deposition of fine sediment with deep rooting and good drainage, which makes these productive soils.
Soil order: Raw
Area: 3%
Key characteristics: Mostly parent material with limited soil development. Highly variable and difficult to summarise. Typically, low in fertility.
Soil order: Gley
Area: 2%
Key characteristics: Poorly drained soil that remains wet unless drained. Medium to high fertility but rooting limited by lack of oxygen at depth.
Soil order: Melanic
Area: 2%
Key characteristics: High natural fertility, well drained and deep soil unless directly over rock. Versatile and productive soils.
The diagram below gives an example of a soil and how it is named at a range of levels across the different old and new soil naming systems used in Aotearoa New Zealand.
The Genetic Soil Classification (GSC) was the first national system for naming soils developed in 1948. This system became outdated when it was used as the foundation for the New Zealand Soil Classification (NZSC) developed in the 1980s. The Fundamental Soil Layer, which was first released in 2000, uses the NZSC to its Group level and is the only modern soil map with national coverage.
The regional soil series names are the finer scale names from the GSC that relate soils to the areas where they are found and allow for more detailed classification than the NZSC. They are still commonly used due to their familiarity. The regional series names are used in the 2004 growOTAGO soil map but are related to the NZSC hierarchy rather than that of the GSC. The series names were modified by S-Map, launched in 2002, which merges series names from different areas that have equivalent soil types, calling the series ‘families’ instead. As a result, the S-map and regional soil series can be the same or different.
If you are trying to convert between naming systems, you can use this tool from Manaaki Whenua Landcare Research which correlates soil names between the regional soil series, NZSC, and S-Map.


Genetic Soil Classification (NZG)
Historic genetic soil classification (NZG) developed by pioneer New Zealand soil scientist, Norman Taylor.

New Zealand Soil Classification (NZSC)
Discover the diversity of New Zealand soils with the New Zealand Soil Classification. Developed by Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research, this system categorizes soils based on physical, chemical, and morphological characteristics

S-Map Online
Explore interactive soil maps of Aotearoa New Zealand with S-Map Online. Access a variety of soil fact sheets containing information about key soil properties and environmental risks.